.hovertable {
font-family: verdana,arial,sans-serif;
font-size:11px;
margin: -2px;
width: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
background: #FFF;
color: #024457;
border:2px solid #167F92;
border-radius: 10px;
border-collapse: separate;
}
.hovertable th {
background-color:#c3dde0;
border-width: 1px;
color:#024457;
padding: 8px;
border-: solid;
border-color: #a9c6c9;
}
.hovertable tr {
border: 1px solid #D9E4E6;
&:nth-child(odd) { // highlight the odd rows with a color
background-color: #EAF3F3;
}
.hovertable td {
border-width: 1px;
padding: 8px;
border-: solid;
border-color: #a9c6c9;
}
summary {
cursor: pointer;
font-size: 16px;
font-weight: bold;
text-decoration-line: underline;
content: « + »;
}
.coin {
background-color:#E4EFFF;
border:1px solid #9FC6FF;
padding:5px;
/*arrondir les coins en haut à gauche et en bas à droite*/
-moz-border-radius:10px;
-webkit-border-radius:10px;
border-radius:10px;
font-family: ‘Trebuchet MS’, Verdana, sans-serif;
}
VB.Net :Tableaux et matrices
| // Généralités
Déclaration et création
Exemple
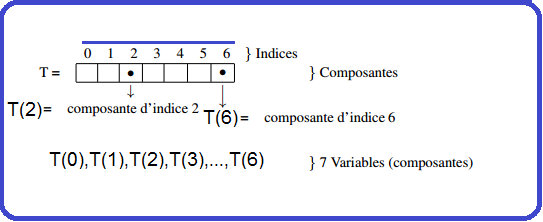
Dim nom_tab ( ) as type <FONT color="green"Exmples: Dim Tableau(3) As Integer Dim Tableau(3) As String Dim Tableau(3) As float … Dim Tableau(3) As Double Image de ce qui est présent en mémoire centrale après ces déclarations

Exemple
‘Déclaration Dim t As String() ‘On instancie et on initialise t = New String(1) {« Un », « Deux »} Image de ce qui est présent en mémoire centrale après ces déclarations
Exemple
Dans cette éventualité VB.Net crée le tableau, calcule sa taille et l’initialise avec les valeurs fournies. Image de ce qui est présent en mémoire centrale après ces déclarations
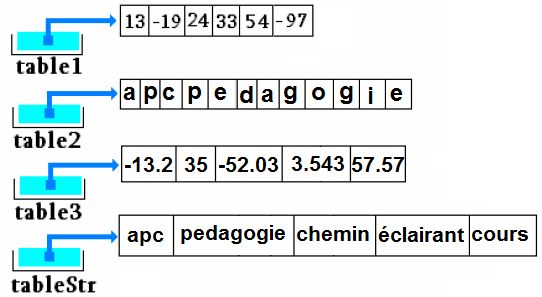
Dim tab() As Apprenant 'Cette ligne ne fait que déclarer un tableau (de taille non spécifiée). tab = New Apprenant (42) ' Instancie un tableau de taille 42
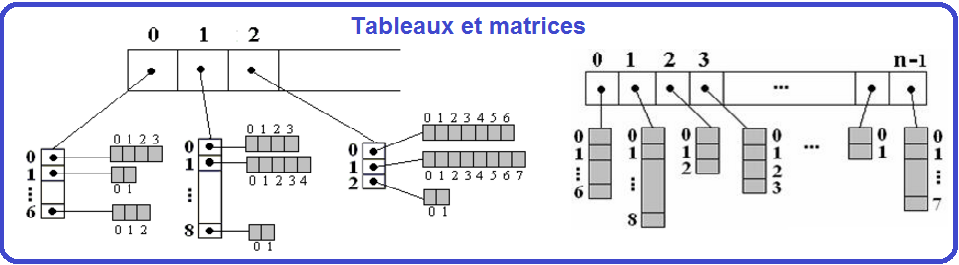
Tableaux à deux dimensions(ou plus)
Dim nom_tab( , ) As type= new type(n, m) {} Dim Tableau(indice de la dernière ligne,indice de la dernière colonne) indice de la dernière colonne)
// Déclarer un tableau à deux dimensions (appelée aussi matrice)
Dim tab1 = new int(2, 3); // 2 lignes, 3 colonnes
//tableau multidimensions de string
string(,) tabString = new string(3, 2) { {"un", "deux"},
{"trois", "quatre"},
{"cinq", "six"} }
// Déclarer et définir les valeurs des éléments du tableau
Dim tab2(,) as int = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } };
// déclaration d'un tableau de 10 lignes et de 20 colonnes
Dim tableauRectangulaire(,) as integer = new integer(10, 20);
Dim tableauRectangulaire(,) As Integer = New Integer(10,20) {}
// Tableaux à deux dimensions.
Dim tab2D(,) As Integer = new Integer(,) { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 }, { 5, 6 }, { 7, 8 } };
// The same array with dimensions specified.
Dim tab2D(,) As Integer = new Integer(4,2) { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 }, { 5, 6 }, { 7, 8 } };
// Tableaux à deux dimensions string.
Dim tab2Db(,) As String = New String(3,2) { { "un", "deux" }, { "trois", "quatre" },{ "cinq", "six" } };
// Tableau en trois dimensions.
Dim tab3D(,,) As Integer = New Integer(,,) {{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}},
{{7, 8, 9}, {10, 11, 12}}};
// Le même tableau avec des dimensions spécifiée2.3 Dim tab3Da(,,) As Integer = New Integer(2,2,3) {{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}},
{{7, 8, 9}, {10, 11, 12}}};
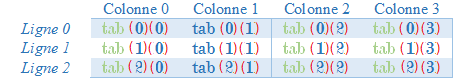
Voici un tableau à 2 dimensions , qui contient 3 lignes et 4 colonnes :
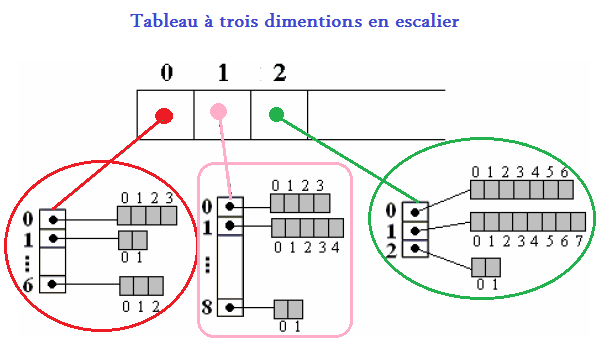
Tableaux de tableaux (en escalier)
Dim tab_escalier ()() As Integer= new integer(5)(){} Dans la déclaration ci-dessus les lignes sont fixées dans la taille. Mais les colonnes ne sont pas spécifiés , car ils peuvent varier. Dim tab_escalier(0) as Integer=new int(3); Dim tab_escalier(1) as Integer= new int(5); Dim tab_escalier(2) as Integer= new int(2); Dim tab_escalier(3) as Integer= new int(8); Dim tab_escalier(4) as Integer= new int(10); Dim tab_escalier(0) as Integer= new int() { 3, 5, 7};
Exercices
|