.hovertable {
font-family: verdana,arial,sans-serif;
font-size:11px;
margin: -2px;
width: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
background: #FFF;
color: #024457;
border:2px solid #167F92;
border-radius: 10px;
border-collapse: separate;
}
.hovertable th {
background-color:#c3dde0;
border-width: 1px;
color:#024457;
padding: 8px;
border-: solid;
border-color: #a9c6c9;
}
.hovertable tr {
border: 1px solid #D9E4E6;
&:nth-child(odd) { // highlight the odd rows with a color
background-color: #EAF3F3;
}
.hovertable td {
border-width: 1px;
padding: 8px;
border-: solid;
border-color: #a9c6c9;
}
summary {
cursor: pointer;
font-size: 16px;
font-weight: bold;
text-decoration-line: overline underline line-through;
}
.coin {
background-color:#E4EFFF;
border:1px solid #9FC6FF;
padding:5px;
/*arrondir les coins en haut à gauche et en bas à droite*/
-moz-border-radius:10px;
-webkit-border-radius:10px;
border-radius:10px;
font-family: ‘Trebuchet MS’, Verdana, sans-serif;
}
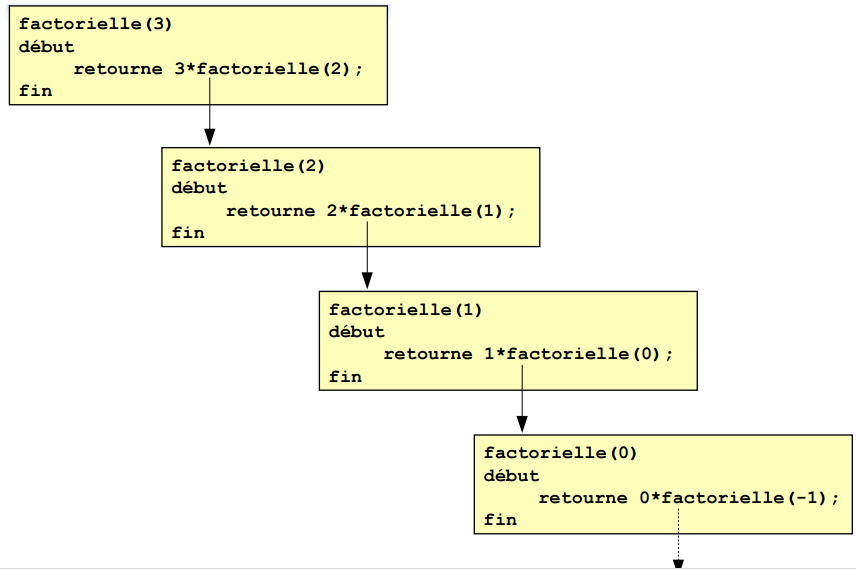
Algorithme: la récursivité
|
| // Définitions
Présentation et utilisations
Applications
Questions :
b) Donner les algorithmes correspondants, c) Traduire l’ensemble en un programme Pascal.
N= donnée (« Donner un entier : ») Fin PP Contenu du chapitre :Algorithme: la récursivité1.Définitions et utilisations Sommaire du cours Algorithme
|
|
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({}); |